 自定义starter
自定义starter
# P6、自定义 starter
我们分析完毕了源码以及自动装配的过程,我们可以尝试自定义一个启动器来玩玩!
# 6.1、说明
启动器模块是一个 空 jar 文件,仅提供辅助性依赖管理,这些依赖可能用于自动装配或者其他类库;
命名归约:
官方命名:
- 前缀:spring-boot-starter-xxx
- 比如:spring-boot-starter-web…
自定义命名:
- xxx-spring-boot-starter
- 比如:mybatis-spring-boot-starter
# 6.2、编写启动器
1、在 IDEA 中新建一个空项目 spring-boot-starter-diy
2、新建一个普通 Maven 模块:kuang-spring-boot-starter
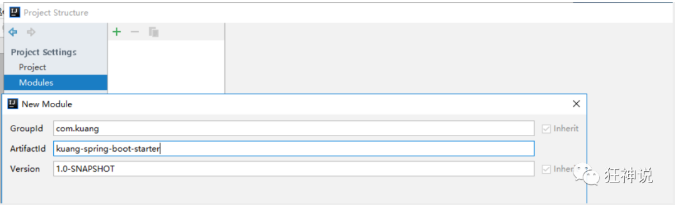
3、新建一个 Springboot 模块:kuang-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure

4、点击 apply 即可,基本结构
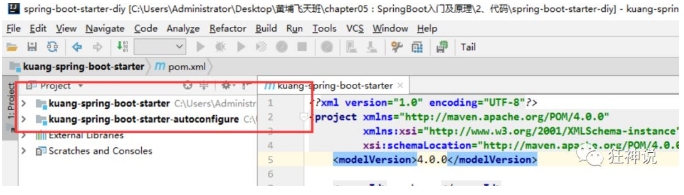
5、在我们的 starter 中 导入 autoconfigure 的依赖!
<!-- 启动器 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入自动配置模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.kuang</groupId>
<artifactId>kuang-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
6、将 autoconfigure 项目下多余的文件都删掉,Pom 中只留下一个 starter,这是所有的启动器基本配置!
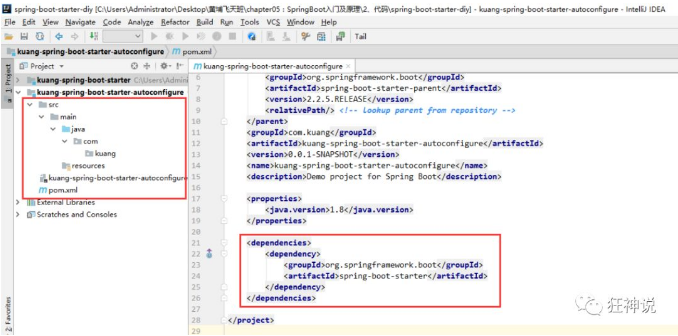
7、我们编写一个自己的服务
package com.kuang;
public class HelloService {
HelloProperties helloProperties;
public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() {
return helloProperties;
}
public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
public String sayHello(String name){
return helloProperties.getPrefix() + name + helloProperties.getSuffix();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
8、编写 HelloProperties 配置类
package com.kuang;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
// 前缀 kuang.hello
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "kuang.hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
public String getPrefix() {
return prefix;
}
public void setPrefix(String prefix) {
this.prefix = prefix;
}
public String getSuffix() {
return suffix;
}
public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
this.suffix = suffix;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
9、编写我们的自动配置类并注入 bean,测试!
package com.kuang;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication //web应用生效
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
HelloService service = new HelloService();
service.setHelloProperties(helloProperties);
return service;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
10、在 resources 编写一个自己的 META-INF\spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.kuang.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
1
2
3
2
3
11、编写完成后,可以安装到 maven 仓库中!
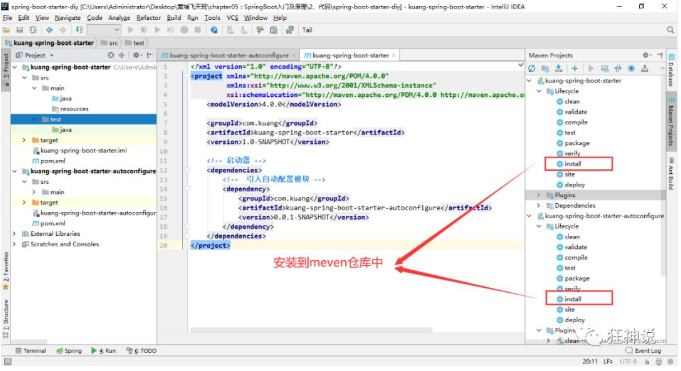
# 6.3、新建项目测试我们自己写的启动器
1、新建一个 SpringBoot 项目
2、导入我们自己写的启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>com.kuang</groupId>
<artifactId>kuang-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
3、编写一个 HelloController 进行测试我们自己的写的接口!
package com.kuang.controller;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return helloService.sayHello("zxc");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
4、编写配置文件 application.properties
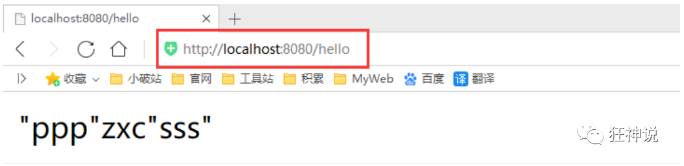
kuang.hello.prefix="ppp"
kuang.hello.suffix="sss"
1
2
2
5、启动项目进行测试,结果成功 !
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2024/06/09, 21:19:54
